|
EKG
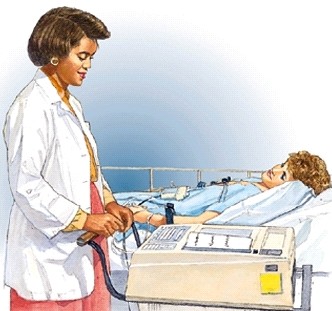
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a safe and inexpensive way for a doctor to monitor a person's heart rate and rhythm. Electrodes (soft sticky patches) are attached to various parts of the body - the chest, wrists, ankles and back. These patches will conduct electrical impulses. The technician will apply a conducting gel to ensure a good connection. They will then hook the electrodes up to the machine and the test begins. It usually lasts less than one minute. The ECG simply records the heart's electrical activity.
|