Stroke in Women
Photos and Images
![]()
List of Pictures
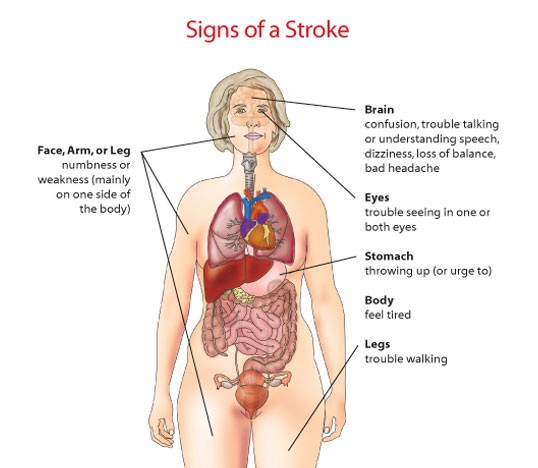
Signs of a Stroke
FAST Signs
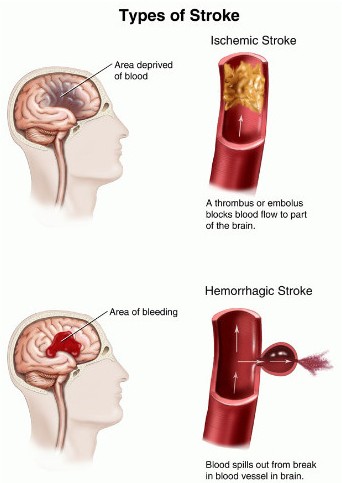
Types of Strokes
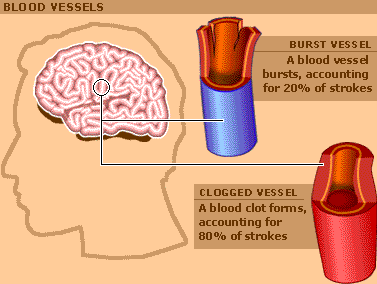
Causes of Strokes
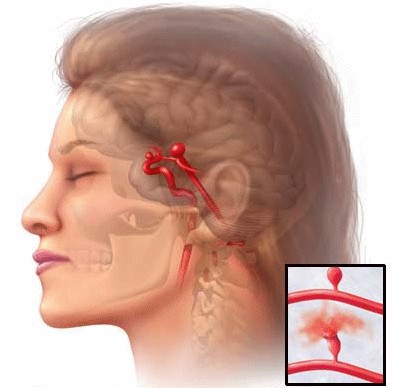
Aneurysms
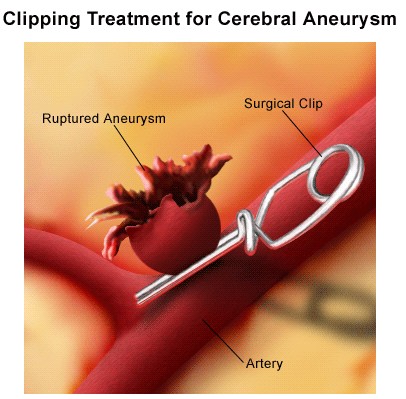
Clipping Surgery For Aneurysms
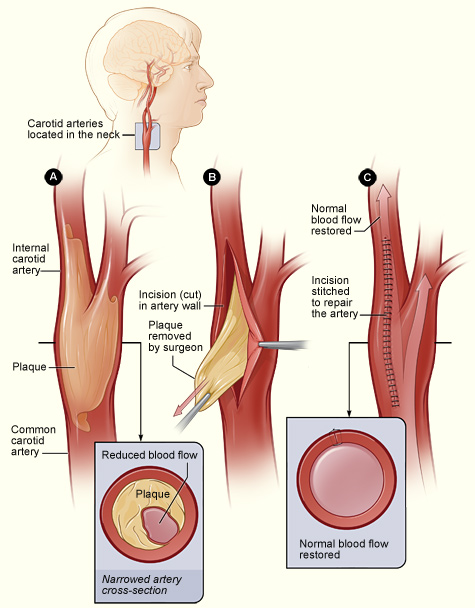
Carotid Endarterectomy
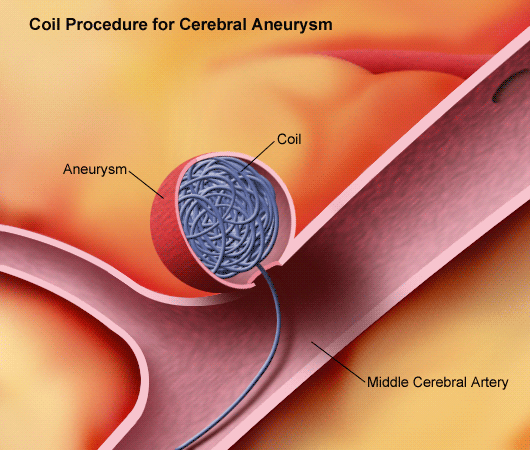
Coil Embolization
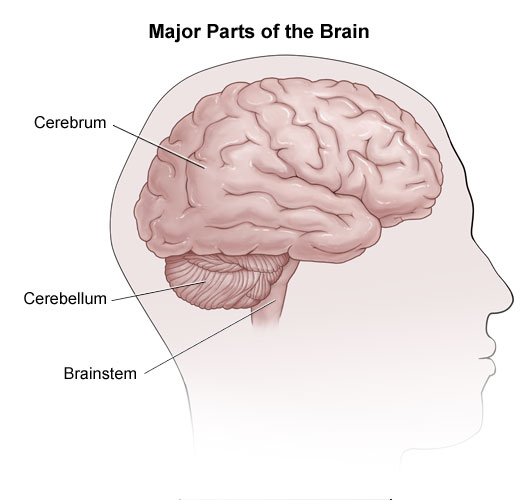
Diagram of the Brain
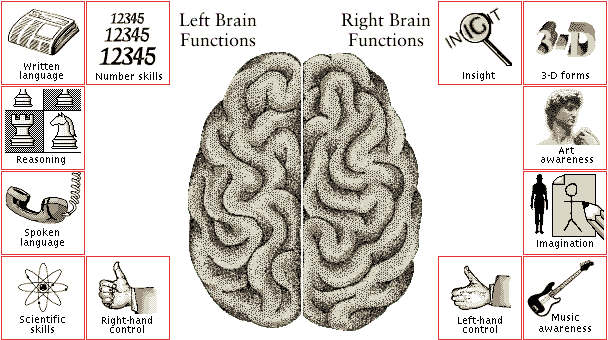
Functions of the Brain