Apgar Score Test
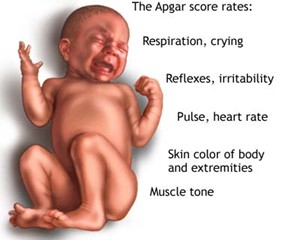
Most newborns are assessed using the so-called APGAR score. This is a quick test carried out 1 and 5 minutes after delivery to speedily determine the health of the baby. The 5 categories assessed are: heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex action and skin color/complexion. Each of these categories is scored between 0 and 2, depending on the observed condition of the newborn. Scores 7 and above are normal, 4 to 6 fairly low, and 3 and below are regarded as critically low.
Say Hello To Baby
Once the APGAR test has been completed your baby will be placed on your abdomen and dried with a warm towel. You will then both be covered with a towel. Early skin to skin contact helps raise the newborn's body temperature and stops they crying. Additionally it facilitates the passing of a bacteria called staphylococcus aureus from the mothers skin into the lungs and tummy of the baby. This helps boost their early immune system so they can fight infections. Your baby may even use this moment to seek a first feeding. This is an ideal time for a lesson on how to breastfeed if you plan to. A nurse will assist you in the process.
|
Within the first 24 hours your baby will undergo a series of tests and screenings. A pediatric hospitalist (pediatrician who works in the hospital setting) will carry out these tests. If not, they will be scheduled for within 5 days of leaving hospital.
Physical Examination
The doctor will assess breathing (the baby must be calm for this examination). He will listen for grunting noises and count the baby's breaths which should be 30 to 60 per minute. He will look at the rise and fall of the chest to see if it is normal.
Movement: He will assess the baby's movements - are they normal and symmetrical?
Skin: Is there any bruising or swelling. Does the skin have normal color and tone? Is it warm to touch? If very cold or warm the baby's temperature will be taken.
Breastfeeding: The doctor will ask how is feeding going and if there are any breastfeeding problems. Is your baby satisfied with the feed and how do your breasts feel?
Signs Of A Well Baby
• Weighs 2,500 g or more.
• Is feeding well and suckling efficiently 8 times in 24 hours, day and night.
• No obvious medical danger signs.
• No special treatments or medications are required.
• If the baby is small, it is feeding well and gaining weight at the correct rate.
Signs Of Infection
The following are signs of infection or other medical issues which need treating:
• Fast breathing (more than 60 breaths per minute).
• Slow breathing (less than 30 breaths per minute).
• Severe gasping for breath or grunting.
• Convulsions.
• Floppiness or stiffness of the body.
• Temperature over 38ºC indicating fever.
• Temperature less than 35ºC which does not rise after warming.
• Pus, redness or swelling of the umbilicus cord stump.
• More than 10 skin pustules (acne type spots on the skin).
• Severe paleness.
Screening for Hearing Problems
Your baby will be screened for hearing problems. These tests are quick, safe and painless. If the baby has fluid or debris in the middle ear, he may need to be tested again. While the chances of hearing loss are small, the sooner an issue is detected the better.
Neonatal/Newborn Screening
Some states require all infants to be tested for certain disorders before being discharged. The doctor will take a drop of blood with a heel-prick from the baby, this will suffice for testing. The results take about 2 weeks to come through. Disorders tested by this screening usually include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, fatty acid oxidation disorders, galactosemia, hyperphenylalaninemia and homocystinuria.
Related Article: Mom's Problems
Postpartum complications: What can go wrong for mom.
Postpartum bleeding: How much is too much?
Postpartum emotions: The ups and downs of motherhood.
Nursing Issues
Breasfeeding milk supply: Diaper chart, how many should be used?
Breastfeeding positions: Which one is best for newborns?
Congenital Heart Disease Screening
Some children are born with a structural defect to their heart. In the first few days of birth, babies with congenital heart disease (CHD) are at serious risk of life threatening complications. Ideally those with the condition will be identified as soon as possible. CHD screening is recommended for all babies, regardless of their risk factor. The test is painless and involves placing a soft sensor around the baby's foot or hand to measure their pulse and the amount of oxygen in their blood (the test is called a pulse oximetry). It only takes a few minutes.
How Long Will We Be In Hospital?
The average hospital stay after a vaginal delivery is 2 days (or 12 to 24 hours for a birthing center). The average hospital stay after a cesarean section delivery is 3 days (birthing centers do not perform c-sections).
Next, read our postpartum baby care tips for looking after your baby at home (and baby car seats for the journey).
|
![]()
